What Are the Key Differences Between Routers and Switches?
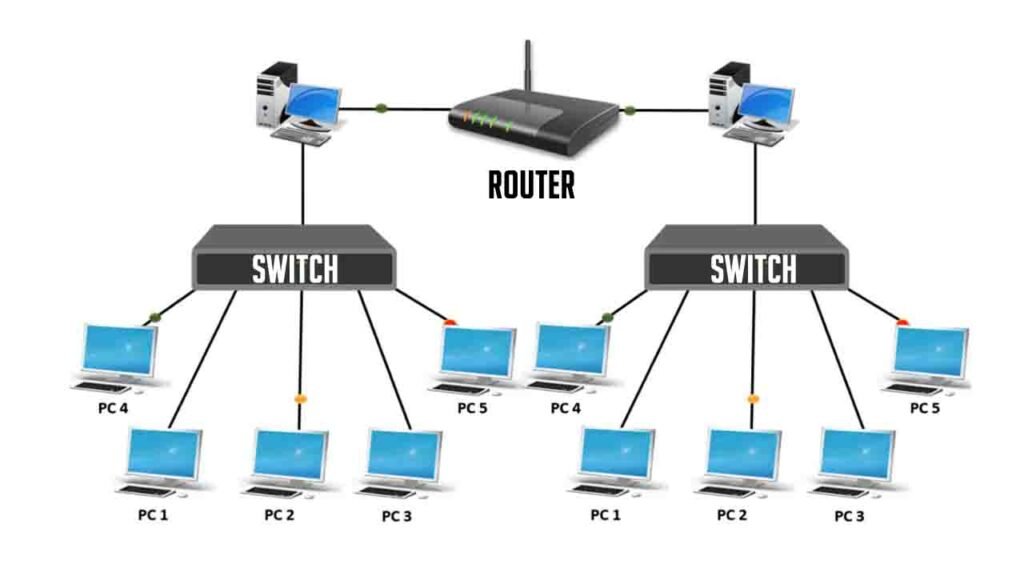
Understanding the roles routers and switches play is crucial for effective network management. These devices are fundamental in networking, yet they serve different purposes and bring different functionalities. By exploring what each does, how they operate, and their key features, you can make informed decisions on how to optimize your network’s performance and security. This article delves into these differences to help you better understand their impact on your network.
What is a Router?
Routers are essential for directing data traffic between different networks, acting as a dispatchers. They manage the flow of data packets, ensuring they reach their destination efficiently.

How Routers Work
Routers connect multiple networks, often linking a local network to the broader internet. They work by analyzing data packets and determining the best route for each one, ensuring it reaches the correct destination. For instance, if a device within a network uses an internal IP, such as “192.168.100.45,” the router uses network address translation (NAT) to manage data flow and secure internal IPs from external access. Routers also handle routing protocols to adapt to network changes, ensuring stable connections for scalable networking.
Key Features of Routers
Routers come equipped with a range of features essential for network performance and security. Key features include IP address management, which allows the router to identify and direct devices on the network, and firewall capabilities to block unauthorized access. Network address translation (NAT) further secures the network by masking private IP addresses. Routers also enable Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize data traffic, enhancing the experience for essential tasks like video conferencing. Connectivity options, such as wired or wireless support, offer flexibility depending on user needs. Some advanced routers support VPNs for encrypted remote access and dynamic routing protocols, enabling seamless connectivity across complex network infrastructures.
Types of Routers
Routers are categorized based on their function and deployment within a network. Core routers are high-performance devices designed for large-scale networks, routing data within a central LAN or WAN. Edge routers operate on the periphery, connecting internal networks to external ones, such as the Internet. Wireless routers combine routing functions with Wi-Fi capability, ideal for homes and small offices. Additionally, virtual routers provide software-based routing solutions, useful for scalable and cloud-based environments. Each type has its unique applications, making it possible to choose a router based on network size, required security features, and budget constraints.
What is a Switch?
Switches are fundamental in managing network communication within a local area network (LAN). They ensure that data packets are sent only to the intended devices within the same network.
How Switches Operate
Switches operate within a local area network (LAN) to direct data traffic between connected devices. They use MAC addresses, a unique identifier for each device, to determine the destination of data frames. This specificity ensures data is sent only to the intended device, reducing unnecessary network congestion. Unlike routers, switches function at the data link layer, working within a single network to keep data traffic local. Some switches support VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to segment traffic for better organization and security. High-performance switches also offer port mirroring, allowing network administrators to monitor data for troubleshooting and network optimization.
Key Features of Switches
Switches are equipped with features that optimize internal network traffic. Key features include port density, allowing multiple devices to connect within a LAN, and bridging capabilities, which prevent unnecessary traffic by sending data only to relevant devices. Managed switches offer additional control, allowing administrators to configure settings, prioritize traffic with QoS, and monitor performance for improved network efficiency. Some switches provide PoE (Power over Ethernet), enabling them to power devices like phones or security cameras directly through network cables. These features make switches invaluable in creating scalable, efficient, and responsive network environments, especially for larger organizations.
Types of Switches
Switches are divided into unmanaged switches, managed switches, and smart switches. Unmanaged switches offer basic connectivity; managed switches provide greater control and settings for traffic management and enhanced features; smart switches offer a balance between unmanaged and managed switches.
How Do Routers and Switches Differ in Networking?
Understanding the operational differences between routers and switches is key to optimizing network performance.
Data Transmission Methods
Routers use IP addresses for routing packets to different networks, whereas switches use MAC addresses within the same network to forward frames directly to devices.
Performance and Speed Differences
Routers can impact network speed due to the need to process and direct traffic between networks. Switches, however, are typically faster as they operate within a single network and handle data frames at the hardware level.
Security Capabilities
Routers offer advanced security features like firewalls and NAT to protect against external threats. Switches, while less focused on security, can still provide basic safeguards like VLANs to segment network traffic.
Which is Better for Your Network Needs?
Choosing between routers and switches depends on your specific networking requirements.
Home Network Requirements
For home networks, a wireless router is often sufficient, providing internet connectivity and basic security features. Switches might be added if there are multiple devices requiring wired connections.
Business Network Requirements
In business environments, a combination of routers and managed switches is preferred. Routers handle external and internal traffic routing, while managed switches offer control and efficiency within the LAN.
Cost Considerations
While routers can be more expensive due to their advanced features, the investment is justified by the security and connectivity they provide. Switches vary in cost based on their management capabilities and number of ports.
Conclusion
Routers and switches serve distinct yet complementary roles in networking. Routers offer connectivity and security across networks, while switches optimize communication within a network. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right devices to meet various network needs, ensuring optimal performance and security. Use this guide to make informed decisions when setting up or upgrading your network infrastructure.






